BPM Full Form is essential in today’s fast-paced business environment. But what exactly is BPM, and why is it so important? Let’s dive into the details to unravel the full form and significance of BPM.
What Does BPM Stand For?
BPM Full Form
BPM Full Form stands for Business Process Management. It’s a comprehensive approach aimed at improving corporate performance by managing and optimizing a company’s business processes.
Various Contexts of BPM
While BPM primarily refers to Business Process Management, it can also denote other terms in different fields, such as Beats Per Minute in music. However, in a business context, BPM is all about streamlining processes to enhance efficiency and productivity.
BPM Full Form in Business Context
Definition and Overview
BPM Full Form Business Process Management is a systematic method of improving an organization’s business processes. It involves analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and optimizing processes to achieve better performance and efficiency.
Key Components of Business Process Management
- Process Design: Crafting the workflow and defining the processes.
- Process Modeling: Visual representation of processes.
- Process Execution: Implementing the process steps.
- Process Monitoring: Tracking the performance of processes.
- Process Optimization: Continuously improving processes based on data.
Benefits of BPM in Business
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlines operations to reduce waste and improve productivity.
- Better Compliance: Ensures processes comply with industry regulations.
- Increased Agility: Allows businesses to adapt quickly to market changes.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhances service delivery and product quality.
The History of BPM Full Form
Evolution of BPM
BPM Full Form has evolved from traditional workflow management systems to sophisticated, technology-driven approaches. Initially, it focused on simple task automation but has grown to encompass complex process optimization across entire organizations.
Key Milestones in BPM Development
- 1960s: Introduction of workflow automation.
- 1990s: Emergence of BPM as a formal discipline.
- 2000s: Integration with digital technologies and ERP systems.
- 2010s: Rise of cloud-based BPM solutions and AI integration.
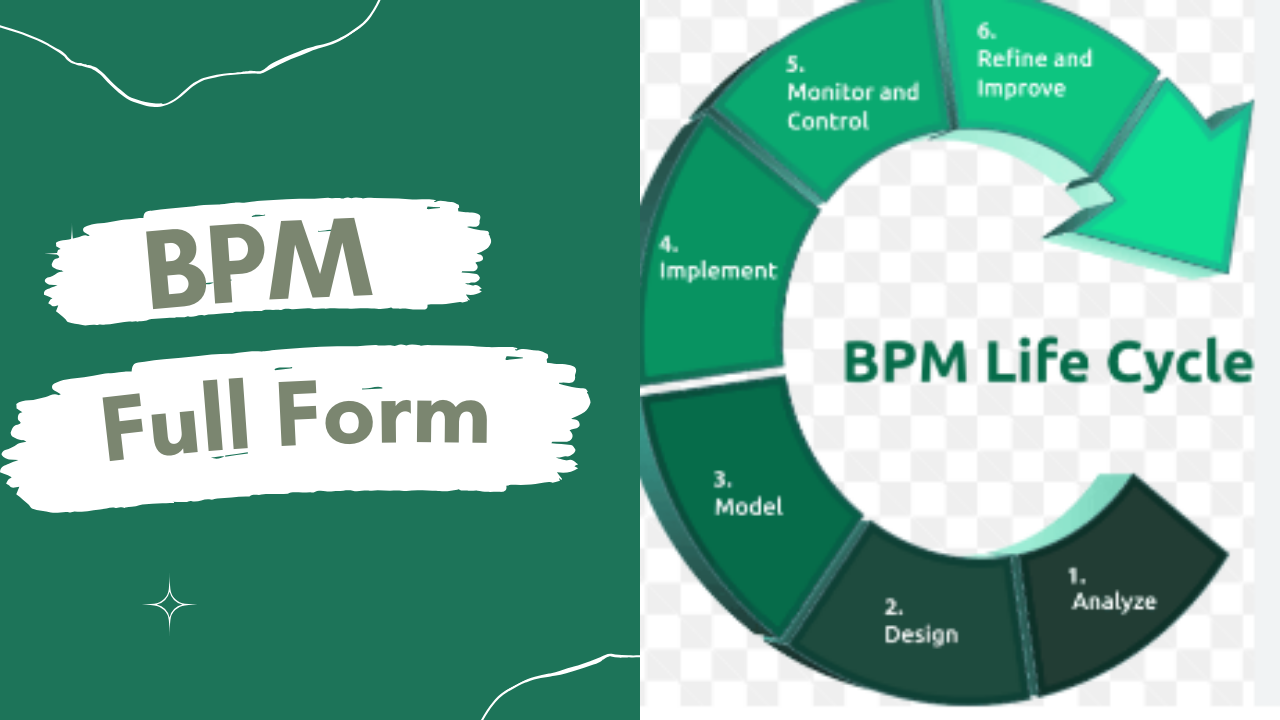
BPM Lifecycle
Design
Designing involves mapping out the existing processes and creating a blueprint for the new, optimized process.
Modeling
Modeling uses tools and software to create visual representations of the processes, allowing for simulation and analysis.
Execution
Execution is the implementation phase where the designed processes are put into action using BPM software.
Monitoring
Monitoring involves tracking the performance of the processes in real-time to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Optimization
Optimization is a continuous process where feedback from monitoring is used to make improvements to the processes.
BPM Methodologies
Lean BPM
Lean BPM focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value in business processes. It’s all about efficiency and effectiveness.
Six Sigma and BPM
Six Sigma integrates with BPM to focus on reducing defects and improving process quality through data-driven techniques.
Agile BPM
Agile BPM applies agile principles to business process management, emphasizing flexibility, customer collaboration, and rapid response to change.
BPM Tools and Software
Top BPM Tools in the Market
Some leading BPM tools include:
- Bizagi
- Appian
- Pegasystems
- IBM BPM
Features of Effective BPM Tools
Effective BPM tools should offer:
- User-friendly interfaces
- Real-time monitoring
- Integration capabilities
- Scalability
- Comprehensive analytics
TCPL Packaging Ltd Share Price 2024, 2025, 2026, 2027, 2028, To 2030
IRCTC Share Price 2024, 2025, 2026, 2027, 2028, 2029, 2030
NHPC Share Price 2024, 2025, 2026, 2027, 2028, 2029 To 2030
Choosing the Right BPM Software
When selecting BPM software, consider your business needs, the tool’s features, ease of use, and cost. It’s essential to choose a solution that aligns with your specific process management requirements.
Implementing BPM Full Form in Your Business
Steps to Implement BPM
- Identify: Recognize the processes that need improvement.
- Analyze: Assess the current performance and identify bottlenecks.
- Design: Create a new, optimized process model.
- Implement: Deploy the new process using BPM tools.
- Monitor: Continuously track the process performance.
- Optimize: Make iterative improvements based on feedback.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Resistance to Change: Mitigate by involving stakeholders early and providing adequate training.
- Complexity: Simplify processes where possible and use user-friendly BPM tools.
- Integration Issues: Ensure the BPM software integrates well with existing systems.
Case Studies of Successful BPM Implementation
Company A
Company A streamlined their supply chain process, resulting in a 30% reduction in operational costs and a 20% improvement in delivery times.
Company B
Company B utilized BPM to enhance their customer service operations, achieving a 50% increase in customer satisfaction and a 25% reduction in response times.
BPM and Digital Transformation
Role of BPM in Digital Transformation
BPM plays a crucial role in digital transformation by providing a framework for process automation, data integration, and continuous improvement, aligning with digital initiatives.
How BPM Supports Digital Initiatives
BPM supports digital transformation by:
- Automating routine tasks
- Integrating disparate systems
- Providing real-time data for informed decision-making
- Enhancing customer experiences through improved processes
BPM vs. Workflow Management
Key Differences
While BPM focuses on end-to-end process optimization, workflow management is more about task automation within a process. BPM Full Form is broader and more strategic, whereas workflow management is tactical.
When to Use BPM vs. Workflow Management
Use BPM when you need comprehensive process improvement across the organization. Opt for workflow management for automating specific tasks within a process.
Future Trends in BPM Full Form
AI and BPM
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing BPM by enabling predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Predictive Analytics in BPM
Predictive analytics in BPM helps forecast future process performance, allowing businesses to proactively address potential issues and optimize outcomes.
The Future of BPM Software
The future of BPM Full Form software lies in greater integration with AI, machine learning, and IoT, providing more intelligent and adaptive process management solutions.
Common Misconceptions about BPM Full Form
BPM Myths Debunked
- BPM is Only for Large Enterprises: BPM benefits businesses of all sizes.
- BPM is Just About Automation: BPM involves strategic process optimization, not just automation.
- BPM is Too Complex: Modern BPM tools are user-friendly and designed to simplify process management.
Understanding the Real Value of BPM
BPM Full Form real value lies in its ability to transform business operations, improve efficiency, and drive sustainable growth through continuous process improvement.
How to Learn BPM Full Form
Resources for Learning BPM
- Books: “Business Process Management: Practical Guidelines to Successful Implementations” by John Jeston and Johan Nelis.
- Online Courses: Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer comprehensive BPM courses.
- Webinars and Workshops: Attend industry webinars and workshops for hands-on learning.
Certifications and Training Programs
- Certified Business Process Professional (CBPP)
- Six Sigma Certification
- BPM Institute’s BPM Certification
Conclusion
BPM Full Form Business Process Management is a vital strategy for any organization aiming to enhance efficiency, agility, and customer satisfaction. By understanding and implementing BPM, businesses can achieve significant improvements in their operations, leading to sustainable growth and success.